Technical SEO might sound like a buzzword thrown around by digital marketers, but it’s actually the backbone of a well-optimized website. Imagine spending hours crafting perfect content only to have it buried under a mountain of technical issues. In 2024, with search engine algorithms evolving faster than ever, understanding the nuances of Technical SEO is more crucial than ever. From crawling and indexing to site speed and mobile optimization, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know to make sure your site isn’t just good, but technically superb!

What is Technical SEO ( Is it Important?)
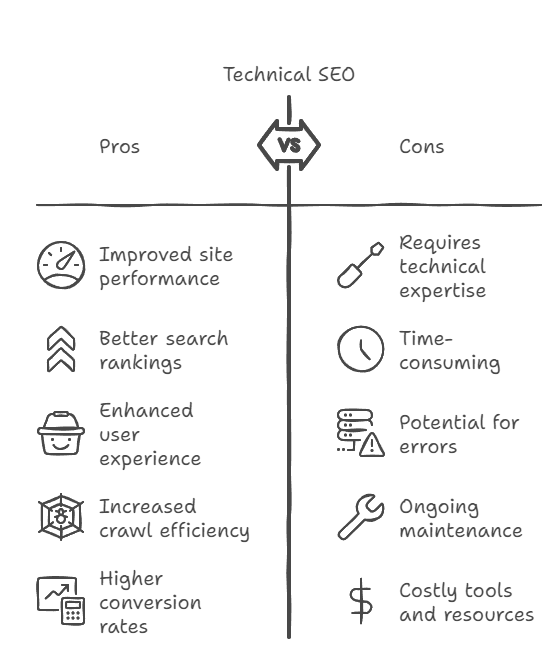
Technical SEO often feels like the elusive part of search engine optimization that many overlook, but it’s absolutely vital for a website’s success. To put it simply, Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website’s infrastructure and backend to help search engines crawl, index, and understand your site better. It’s like setting up a well-organized filing system for a massive library—without it, finding and accessing your content becomes a nightmare.
Definition of Technical SEO
At its core, Technical SEO encompasses all the non-content-related aspects of your website that impact its visibility in search engine results. This includes optimizing elements like site speed, mobile-friendliness, site architecture, and more. It’s not just about making your site look good; it’s about making sure it runs efficiently and is easily accessible to search engines.
Role of Technical SEO in Overall SEO Strategy
You might have the best content on the internet, but if your site isn’t technically sound, that content won’t get the visibility it deserves. Think of Technical SEO as the foundation of a house. Without a strong foundation, even the most beautiful house won’t stand the test of time. Similarly, without robust Technical SEO, your site’s performance and rankings can falter, no matter how great your content is.
Benefits for Website Performance and Search Rankings
Here’s where things get exciting—good Technical SEO can have a direct impact on your website’s performance and search engine rankings. For instance, improving your site’s load speed can significantly enhance user experience, reducing bounce rates and boosting engagement. A well-structured site makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your pages, which can lead to better rankings and more organic traffic.
Optimizing Site for Better Crawling and Indexing
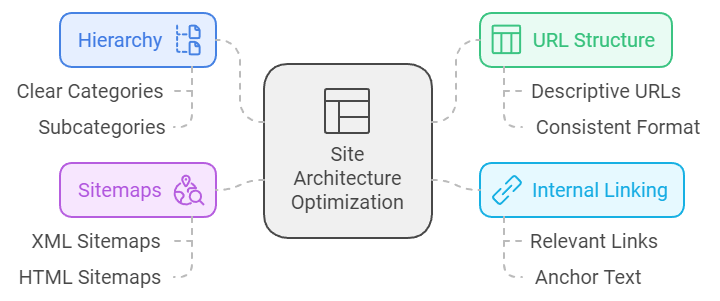
Imagine wandering through a massive library without any cataloging system. You’d be lost in a sea of books with no way to find what you need. That’s what it’s like for search engines when your site architecture isn’t optimized. Proper site architecture is essential for ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your content, which in turn impacts your site’s visibility and rankings.
Importance of a Clear Site Hierarchy
A well-organized site hierarchy is crucial for both user experience and SEO. Think of it like the blueprint of a building. When search engines crawl your site, they follow links to discover and index your pages. A clear hierarchy helps them understand the relationship between different pages and prioritize the most important ones. For example, a logical structure might include a homepage, followed by main category pages, and then subcategories or individual posts.
How to Create and Use XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is like a detailed map for search engines. It lists all the pages on your site that you want to be indexed, making it easier for crawlers to find and prioritize your content. Creating and submitting an XML sitemap through Google Search Console or other tools is a straightforward process, but it’s incredibly effective. You can use plugins like Yoast SEO for WordPress to generate sitemaps automatically, saving you time and ensuring that all your pages are included.
Managing URL Structures and Canonicalization
URL structure is another critical element of site architecture. Clean, descriptive URLs are not only better for users but also for search engines. Avoid using long, complex URLs with unnecessary parameters. Instead, opt for short, keyword-rich URLs that clearly describe the page content.
For instance, a URL like www.example.com/technical-seo-tips is much more user-friendly and SEO-friendly than www.example.com/index.php?id=12345.
Canonicalization is another important aspect to consider. It helps prevent duplicate content issues by telling search engines which version of a page is the “canonical” or preferred version. This is crucial if you have multiple pages with similar or identical content. Using the rel="canonical" tag in your HTML code directs search engines to the primary version, ensuring that your content is properly indexed and credited.
Practical Tips for Optimizing Site
- Organize Your Content: Group related content into categories and subcategories. This helps both users and search engines navigate your site more easily.
- Use Internal Linking: Create a network of internal links to help users and search engines discover related content. This also spreads link equity throughout your site.
- Regularly Audit Your Site: Periodically review your site’s structure to ensure that it’s still effective. Look for broken links, outdated content, or any changes that might impact navigation.
I remember working on a site where the URL structure was a mess. After cleaning it up and implementing a clear hierarchy, not only did user engagement improve, but search engines started indexing pages more effectively. It was a game-changer for their SEO strategy.
Enhancing Website Speed and Performance
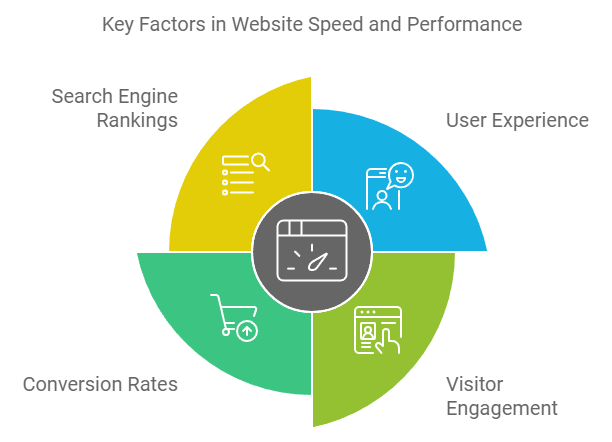
Speed is everything. Imagine clicking on a link and waiting forever for a page to load—it’s frustrating, right? This is why enhancing website speed and performance is crucial not only for user satisfaction but also for SEO. Google and other search engines factor page speed into their ranking algorithms, meaning a slow site can negatively impact your search rankings. Here’s how to tackle this issue effectively.
The Impact of Site Speed on SEO and User Experience
Site speed directly affects user experience. Studies show that even a one-second delay in page load time can lead to higher bounce rates and lower user satisfaction. This means fewer people stick around to read your content or engage with your site. From an SEO perspective, search engines like Google use page speed as a ranking factor. A faster site is likely to rank better and attract more organic traffic.
Tools for Measuring Website Speed
Before you can improve your site’s speed, you need to measure it. Several tools can help you analyze your site’s performance and pinpoint areas for improvement. Google PageSpeed Insights is a popular choice, providing detailed reports on both mobile and desktop performance. Other useful tools include GTmetrix and Pingdom, which offer insights into load times and suggestions for optimization.
Practical Tips for Improving Load Times
- Optimize Images: Large image files can significantly slow down your site. Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to compress images without sacrificing quality. Also, consider using responsive images that adjust to different screen sizes.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Browser caching allows frequently accessed resources to be stored locally on a user’s device, so they don’t need to be reloaded each time they visit your site. Configure your caching settings in your server or through a caching plugin.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Each element on a page (like images, scripts, and stylesheets) requires an HTTP request. Reduce the number of elements on your page to lower the total number of requests. Combine CSS and JavaScript files where possible to streamline the loading process.
- Enable GZIP Compression: GZIP compression reduces the size of your website’s files, making them faster to transfer from your server to the user’s browser. Most modern web servers support GZIP compression, and it’s relatively easy to enable.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN distributes your site’s content across multiple servers around the world, reducing the distance data has to travel and speeding up load times for users regardless of their location.
Personal Experience with Site Speed Optimization
I once worked with a client who was struggling with slow load times. Their site had large, unoptimized images and a cluttered codebase. After implementing image compression, enabling GZIP, and setting up a CDN, we saw their load times cut in half. The impact was immediate: bounce rates dropped, user engagement improved, and their rankings started to climb. It was a clear example of how critical speed is for both user experience and SEO.
Mobile-Friendliness and Responsive Design
Ensuring your website is mobile-friendly isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity. With more and more users accessing the web from their mobile devices, a site that isn’t optimized for mobile can result in lost traffic and lower rankings. Here’s how to make sure your website delivers a seamless experience across all devices.
Mobile-First Indexing and Its Significance
Google has shifted to mobile-first indexing, which means the search engine primarily uses the mobile version of a website for indexing and ranking. This change underscores the importance of mobile optimization. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, it could negatively affect your search engine rankings. The mobile-first approach means that if your mobile site is lacking, it might impact how your desktop site is perceived by search engines as well.
Best Practices for Responsive Web Design
Responsive design ensures that your website adjusts smoothly to various screen sizes, from smartphones to desktops. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Fluid Grids: Use fluid grids to create layouts that adapt to different screen sizes. This means using relative units like percentages instead of fixed units like pixels to define the size of elements on your page.
- Flexible Images: Make sure your images scale correctly on different devices. Use CSS to set the maximum width of images to 100% of their container to ensure they don’t overflow or appear distorted.
- Media Queries: Utilize media queries to apply different styles based on device characteristics, such as screen width, height, and orientation. This allows you to customize the user experience depending on the device being used.
- Touch-Friendly Design: Consider the touch interface when designing mobile elements. Make sure buttons are large enough to be easily tapped and that there’s enough spacing between interactive elements to avoid accidental clicks.
Tools to Test Mobile Usability
Testing your site’s mobile usability is crucial to ensure it performs well across different devices. Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool is a straightforward option to check how your site fares on mobile devices. It provides insights into any issues and suggestions for improvement. Additionally, tools like BrowserStack or Responsinator let you preview how your site looks on various devices and screen sizes.
Personal Experience with Mobile Optimization
I remember a time when a client’s website wasn’t optimized for mobile, and it was a huge pain point. Their desktop site looked great, but on mobile, it was a disaster—elements were misaligned, and the text was barely readable. After redesigning the site with a responsive layout and conducting thorough mobile testing, we saw an immediate improvement in user engagement and a boost in mobile traffic. It was a clear reminder of how vital mobile optimization is.
Improving Site Security with HTTPS

Site security is more crucial than ever. Users and search engines alike are paying close attention to how secure websites are. One of the most straightforward and impactful ways to enhance your site’s security is by implementing HTTPS. Here’s why HTTPS matters and how you can make the switch.
Why HTTPS is Crucial for SEO
HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is an extension of HTTP. It adds a layer of security by encrypting the data exchanged between users and your website. Google has explicitly stated that HTTPS is a ranking signal, meaning that sites using HTTPS are likely to receive a ranking boost compared to their HTTP counterparts. Beyond SEO, HTTPS helps protect sensitive information such as login credentials and payment details, which is crucial for maintaining user trust and complying with data protection regulations.
Steps to Implement HTTPS on Your Site
- Obtain an SSL Certificate: To enable HTTPS, you need an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. This can be purchased from a certificate authority (CA) or obtained for free from services like Let’s Encrypt. Your web hosting provider often offers SSL certificates as part of their services, making it easier to set up.
- Install the SSL Certificate: Once you have the certificate, the next step is to install it on your web server. This process varies depending on your hosting provider and server type, but most hosts provide detailed instructions or support to help you through it.
- Update Your Site to Use HTTPS: After installing the SSL certificate, you’ll need to update your website’s URLs to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. This includes updating internal links, scripts, and resources to ensure that they all load securely. Additionally, update your content management system (CMS) settings to reflect the new HTTPS URLs.
- Set Up 301 Redirects: To ensure that users and search engines are directed to the HTTPS version of your site, set up 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS. This informs search engines that your site has permanently moved to a new URL, helping to maintain your search rankings and avoid broken links.
- Update External Links and Sitemaps: Don’t forget to update any external links pointing to your site and submit your updated XML sitemap to search engines. This helps ensure that search engines are aware of the change and can index your site correctly.
Troubleshooting Common HTTPS Issues
Switching to HTTPS might come with a few hiccups. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
- Mixed Content Errors: These occur when your site loads some resources (like images or scripts) over HTTP while the page itself is served over HTTPS. Use tools like Why No Padlock to identify and fix mixed content issues by updating URLs to HTTPS.
- SSL Certificate Errors: If users are encountering SSL certificate errors, double-check that your certificate is correctly installed and not expired. Some issues can be resolved by clearing browser cache or reconfiguring server settings.
Personal Experience with HTTPS Implementation
I had a project where a client’s site wasn’t using HTTPS, and they were seeing a decline in user trust and SEO performance. After guiding them through the process of obtaining and installing an SSL certificate, and updating their site to use HTTPS, we saw a noticeable improvement. Not only did their search rankings recover, but users also felt more secure engaging with their site.
Fixing Common Technical SEO Issues
Technical SEO can sometimes feel like a labyrinth of issues, but tackling common problems head-on can significantly improve your website’s performance and search engine visibility. From broken links to duplicate content, addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining a healthy, SEO-friendly site. Let’s dive into some of the most common technical SEO problems and how to fix them.
Identifying and Resolving Broken Links
Broken links, also known as dead links, occur when a link on your site points to a page that no longer exists. This can frustrate users and negatively impact your SEO. Here’s how to address broken links:
- Find Broken Links: Use tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Ahrefs to crawl your site and identify broken links. Google Search Console also offers a “Coverage” report that highlights crawl errors, including broken links.
- Fix Broken Links: Once identified, you have a few options:
- Update the Link: If the target page has moved, update the link to point to the new location.
- Redirect the Link: If the page no longer exists, set up a 301 redirect to a relevant page or your homepage.
- Remove the Link: If neither updating nor redirecting is feasible, remove the broken link from your site.
Handling Duplicate Content and Thin Content
Duplicate content occurs when the same or very similar content appears on multiple pages within your site or across different sites. This can confuse search engines and dilute your SEO efforts. Here’s how to manage it:
- Find Duplicate Content: Use tools like Copyscape or Siteliner to identify duplicate content on your site. Google Search Console can also help by highlighting duplicate meta descriptions and titles.
- Resolve Duplicate Content:
- Canonicalization: Use the
rel="canonical"tag to indicate the preferred version of a page when you have similar content. This tells search engines which version to index and rank. - Content Consolidation: If you have multiple pages with similar content, consider merging them into a single, comprehensive page.
- Noindex Tags: For duplicate content that doesn’t need to be indexed, use the
noindexmeta tag to prevent search engines from including it in search results.
- Canonicalization: Use the
Monitoring and Fixing Crawl Errors
Crawl errors occur when search engines encounter issues while trying to access your site’s pages. These errors can prevent your pages from being indexed, impacting your SEO. Here’s how to handle crawl errors:
- Identify Crawl Errors: Use Google Search Console’s “Coverage” report to find crawl errors. This report will show you which pages have issues and what types of errors are occurring.
- Fix Crawl Errors:
- 404 Errors: If a page is returning a 404 error (not found), either restore the page if it was mistakenly deleted or set up a 301 redirect to a relevant page.
- Server Errors: If your site is returning server errors (5xx errors), check your server logs and consult with your hosting provider to resolve the issue.
- Blocked Resources: Ensure that important resources like CSS and JavaScript files aren’t blocked by your
robots.txtfile, as this can prevent search engines from properly rendering your pages.
Personal Experience with Technical SEO Issues
I once worked on a site where broken links were causing a significant drop in user engagement and SEO performance. After systematically identifying and fixing these links, and addressing duplicate content issues, the site’s performance improved dramatically. It was a great reminder of how these technical issues, while sometimes minor in appearance, can have a big impact on overall site health.
Optimizing for Voice Search and Featured Snippets
Voice search and featured snippets are becoming increasingly significant in the world of SEO. With the rise of virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, optimizing for voice search can help your content stand out and reach users who are searching with voice commands. Similarly, featured snippets can position your content at the very top of search results, providing valuable visibility. Here’s how to optimize for both.
Understanding Voice Search
Voice search is transforming how people find information online. Instead of typing queries, users speak their questions or commands. This shift means that optimizing for voice search requires a different approach compared to traditional text-based SEO.
- Focus on Natural Language: Voice searches tend to be longer and more conversational than typed searches. Optimize your content to answer specific questions in a natural, conversational tone. For instance, if you’re targeting the query “How can I improve my website’s SEO?” you might write an answer that directly responds to this question in a natural, user-friendly manner.
- Use Structured Data: Structured data, also known as schema markup, helps search engines understand the context of your content. Implementing structured data can improve your chances of appearing in voice search results, as it makes it easier for search engines to pull relevant information for voice queries.
- Optimize for Local Search: Many voice searches are local in nature, such as “best coffee shop near me.” Ensure your business is optimized for local SEO by claiming and updating your Google My Business listing, and including local keywords in your content.
Crafting Content for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are concise answers that appear at the top of Google’s search results, often in a box or a “position zero” slot. They provide quick answers to users’ queries and can significantly boost your visibility.
- Identify Snippet Opportunities: Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to identify which keywords have featured snippets. Analyze the snippets for these queries to understand what type of content is being featured, such as lists, paragraphs, or tables.
- Structure Your Content for Snippets: Format your content to align with common snippet types:
- Paragraph Snippets: Provide clear, concise answers to questions in a well-structured paragraph.
- List Snippets: Use bullet points or numbered lists to present information in a way that’s easy to digest.
- Table Snippets: Include tables with organized data if it suits the type of query you’re targeting.
- Use Header Tags Effectively: Break your content into sections with descriptive header tags (H1, H2, H3) to help search engines understand the structure and relevance of your content. This can improve your chances of being featured in snippets.
- Optimize for the “People Also Ask” Box: This feature shows related questions to the original query. Optimize your content to address related questions and include variations of your target keywords to increase the chances of appearing in this section.
Personal Experience with Voice Search and Featured Snippets
I had a project where optimizing for voice search made a huge difference. By focusing on conversational keywords and restructuring content to answer specific questions, the site saw a significant boost in voice search traffic. Similarly, tweaking content to fit featured snippet formats helped the client achieve a coveted position zero spot, leading to increased visibility and clicks.
Conclusion:
Technical SEO is more than just a set of practices; it’s an ongoing process of ensuring that your website operates smoothly and ranks well. By mastering the basics and exploring advanced tactics, you’ll set your site up for success in 2024 and beyond. Dive into these techniques and start optimizing—your website’s performance and visibility will thank you!

